7-Different Types Of Cricket Bowling Machines
Published: 18 Nov 2024
Bowling machines are essential tools for cricket practice, allowing batters to hone their skills against consistent deliveries. There are several types of bowling machines, each designed with different features and technologies to simulate various bowling styles, speeds, and conditions. Here’s an overview of the different types of bowling machines available
Note: this post contains 2 affiliate links
1. Arm Action (Mechanical Arm) Bowling Machines
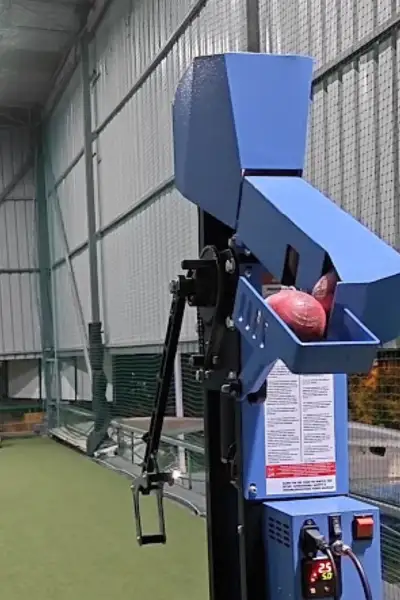

These machines work like the motion of a bowler’s arm, delivering the ball as if it’s being bowled by a human.
- Key Features:
- Utilizes a mechanical arm to simulate the bowler’s action.Allows for variable line, length, and speed.
- Can deliver swing, seam, and spin by adjusting the release angle and speed of the arm.
- Pros: Resembles to actual bowling action due to it’s arm and thus looks more realistic; better suited for batters who want to practice fast bowling.
- Examples: Bola Arm, Paceman Bowling Arm.
2. Two-Wheel Bowling Machines
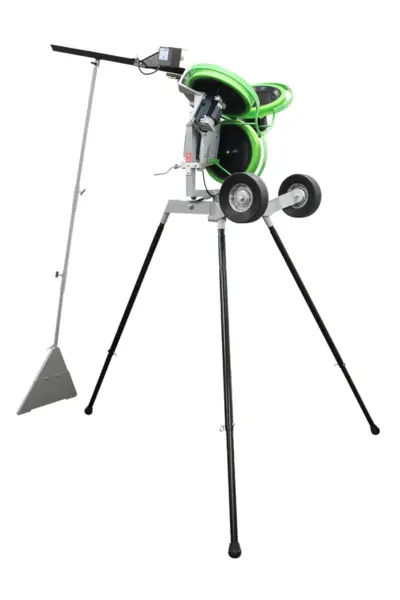

This is the most common type of bowling machine; these machines use two wheels rotating at adjustable speeds to move the ball.
- Key Features:
- The wheels can spin independently at different speeds to produce swing or spin. Capable of delivering fast balls (up to 160 km/h), swing, seam, and spin.
- Adjustments allow for variations in speed, bounce, and delivery angle.
- Pros: Highly versatile; allows for practicing against fast bowling, spin, and swing.
- Cons: Requires more setup and calibration.
- Examples: Bola Professional, JUGS Cricket Machine.
3. Three-Wheel Bowling Machines
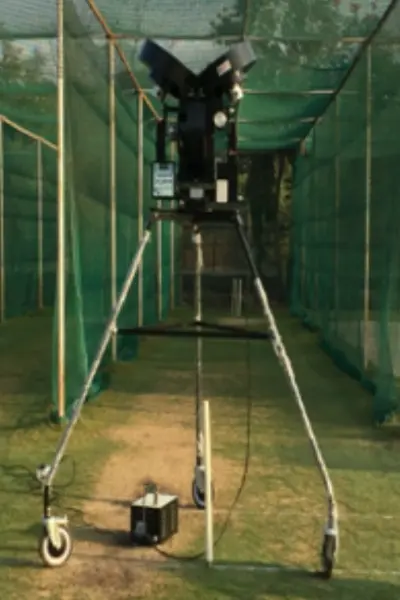

These machines use three wheels to offer even greater control over the ball’s trajectory and spin.
- Key Features:
- Superior control over swing and spin deliveries.
- Can deliver balls with variable bounce, speed, and line.
- Able to simulate reverse swing and more complex deliveries.
- Pros: Advanced control makes it ideal for practicing against diverse deliveries.
- Cons: More complex to operate and more expensive.
- Examples: Leverage Master Digi, Trueman Three-Wheel Machine.
4. Friction Plate (Rotary Disk) Bowling Machines
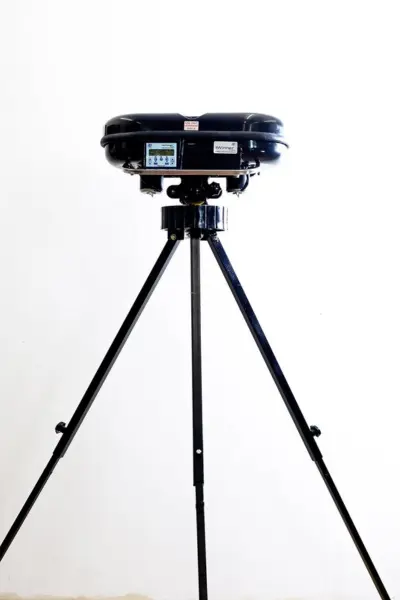

These machines use a rotating friction plate to propel the ball.
- Key Features:
- Capable of delivering fast deliveries and variations like swing or spin.
- Less wear and tear on balls compared to wheel-based machines.
- Adjustable speeds and spin settings.
- Pros: Consistent ball release; less ball damage.
- Cons: Less commonly used than wheel-based machines.
5. Air Cannon (Compressed Air) Bowling Machines
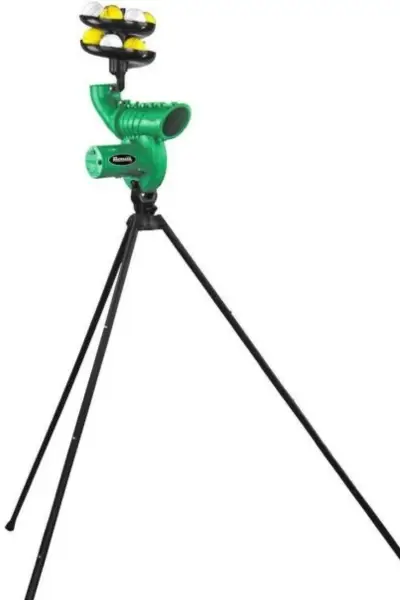

These machines use compressed air to shoot the ball out at high speed.
- Key Features:
- Can deliver at extremely high speeds, often used for specific speed training.Minimal ball wear due to the absence of wheels.
- Simple design with fewer moving parts.
- Pros: Ideal for high-speed practice; less maintenance.
- Cons: Limited ability to deliver spin or swing; mostly focuses on pace.
- Examples: Feed Buddy, Slingshot Speed Gun, Heater Sports.
6. Programmable (Digital) Bowling Machines
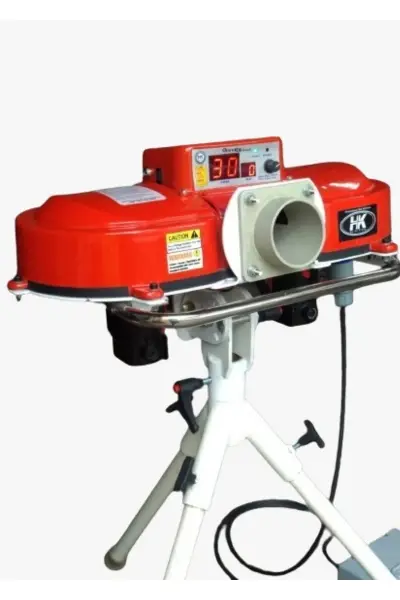

Advanced machines with digital controls allow coaches to pre-program sequences of different deliveries.
- Key Features:
- Allows players to simulate match scenarios with variations in speed, line, and length.
- Capable of delivering different types of deliveries automatically in succession.
- Can store delivery patterns and settings for individual training sessions.
- Pros: Ideal for high-level players looking to simulate match-like scenarios.
- Cons: Expensive and complex to operate.
- Examples: Merlyn Spin Bowling Machine, Leverage Master Digi, .
7. Manual (Handheld) Bowling Machines
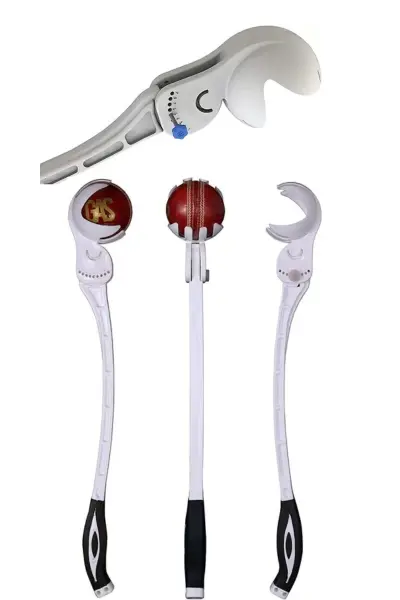
Simple, handheld devices that help coaches and bowlers deliver consistent balls manually.
- Key Features:
- Usually spring-loaded or mechanical lever-based for ball delivery.
- Requires manual operation, making it ideal for specific training drills.
- Pros: Affordable, portable, and easy to use.
- Cons: Limited to slower speeds and consistency.
- Examples: Sidearm Pro, RoboArm, Crompack.
Comparison Table
| Type | Speed Range | Capabilities | Pros | Cons |
| Arm Action | Medium | Swing, seam, spin | Realistic simulation | Limited speed variations |
| Two-Wheel | Medium to High | Fast, spin, swing | Versatile, consistent | More wear on balls |
| Three-Wheel | Medium to High | Fast, swing, spin, reverse swing | Advanced control | Expensive, complex |
| Friction Plate | Medium to High | Swing, spin | Consistent ball release | Less versatile |
| Air Cannon | High | Pure pace | Minimal ball wear | Limited spin capabilities |
| Programmable | Low to High | Custom delivery sequences | Ideal for match simulation | High cost, complex setup |
| Manual | Low to Medium | Swing, spin | Affordable, portable | Limited speed |
Which Bowling Machine Should You Choose?
- Beginners & Casual Players: Manual or arm-action machines are cost-effective and simpler.
- Intermediate Players: Two-wheel machines provide a balance of control and versatility.
- Advanced Players & Professionals: Three-wheel and programmable machines offer the most realistic match scenarios and customization.
Final Thoughts
Each type has its benefits depending on your training needs, skill level, and budget.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks




